Prehospital epinephrine may reduce biphasic reaction and decrease ED length of stay in pediatric anaphylaxis patients: Study
Prehospital epinephrine may reduce biphasic reaction and decrease ED length of stay in pediatric anaphylaxis patients suggests a study published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.
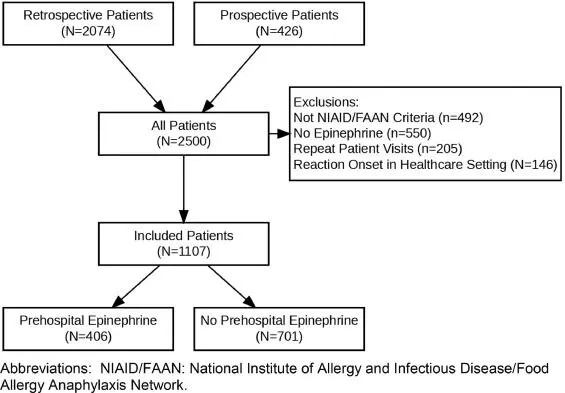
Prompt epinephrine administration is important to improve outcomes in anaphylaxis. The objective of our study was to assess the impact of prehospital epinephrine on clinical outcomes of hospital admission, biphasic reactions, and ED length of stay (LOS) in a cohort of ED anaphylaxis patients including both children and adults. They conducted a single-center prospective and retrospective cohort study of anaphylaxis patients from April 2008 to December 2022. Associations between prehospital epinephrine administration with biphasic reactions and ED LOS were assessed with univariable models and the association with ED disposition was assessed with both univariable and multivariable logistic regression.
Results: A total of 1107 patient visits were included for analysis. The median patient age was 29 (IQR 14-50), 593 (53.6%) patients were female, 366 (33.1%) were under 18 years of age. Patients in the prehospital epinephrine group were also less likely to experience a biphasic reaction (5.4% vs 9.3%; OR 0.56, 95% CI 0.34–0.92) and had a decreased ED LOS (median 4.0 hours vs 4.7 hours). There was no difference in hospital admission between patients with and without prehospital epinephrine in both the univariable (19.5% vs 15.7%; OR 1.30, 95% CI: 0.94–1.79) and multivariable (aOR 1.08, 95% CI: 0.71-1.64) models. Prehospital epinephrine administration reduced the odds of a biphasic reaction and decreased ED LOS but did not reduce hospitalization in this cohort of ED anaphylaxis patients. Our findings suggest that timely administration of prehospital epinephrine is associated with improved patient outcomes.
Keywords:
Reference:
Andrea L. Hlady, Aliza F. Weinman, Yuedan Zhang, Aidan F. Mullan, Ronna L. Campbell,
Outcomes Associated with Prehospital Epinephrine in Adult and Pediatric Anaphylaxis Patients. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. 2024. ISSN 1081-1206,
https://ift.tt/zrpC3sV.
(https://ift.tt/j4zX1WR)
Keywords:
Prehospital, epinephrine, reduce, biphasic, reaction, decrease, ED, length of stay, pediatric, anaphylaxis, patients, study, Anaphylaxis; Emergency Department; Epinephrine; Prehospital Treatment; Pediatric; Biphasic; Hospitalization
from Medical News, Health News Latest, Medical News Today - Medical Dialogues | https://ift.tt/AHdDLs3
Comments
Post a Comment